Cap and Trade in the US Economy
Cap-and-trade, a market-driven way to cut down on pollution, sets an upper limit on the cumulative emissions and permits companies to sell and buy the permits to achieve that level. It has been implemented in numerous programs (California AB 32 is one of them, along with the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative), being simultaneously flexible and encouraging environmental interests.
This post examines the workings of the cap-and-trade policy, its possible economic impact on the economy of the U.S., how it interacts with the tax system, and what the most relevant issues are to consider both by businesses and policymakers regarding this dynamic new regulatory environment. Find a crypto tax lawyer if you want some professional help.
What are the Basics You Must Know About Cap and Trade?
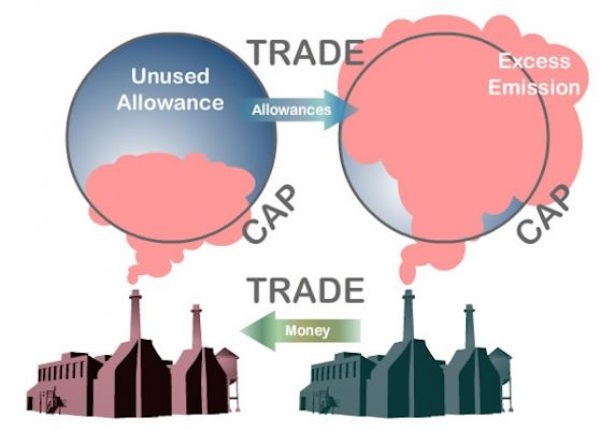
In cap-and-trade, there is a fixed limit of emissions, where the government tries to lower the level of emissions as time moves on. The firms receive or get to buy permits, each of which enables them to produce an allowed amount of CO2. The companies that emit less than they are allowed are able to sell the remaining permits to those who are in excess of their quota, forming a monetary case to cut.
In order to comply, companies are supposed to possess sufficient permits that are equivalent to their emissions; otherwise, they would be fined because they do not have effective coverage in case of exceeding the cap.
Who are the Key Players in The Game?
The government establishes caps on emissions, checks compliance, and auctions permits. The companies have to remain within boundaries or give up their permits in order not to face the punishment. Financial markets allow the purchase and sale of these permits, as traders would purchase and sell any tradable commodity.
Read Also: How Charlotte Business Brokers Simplify Buying a Business
What are Some Potential Economic Impacts We Will Have?
There are good economic implications of cap and trade.
- This encourages firms to spend money on clean technologies to reduce the need for permits, a form of innovation.
- The revenue that is generated by the government through the permit auctions can either be used in renewable energy production or to pay taxes.
- The system motivates efficient businesses, enabling them to generate income by selling unused permits.
- Besides, it lowers the risk of long-term healthcare expenses and environmental degradation by reducing emissions, which is favorable to the health of people and the overall economy.
Negative Aspects
Challenges might also arise from the use of the cap and trade.
- Steel and cement industries, which are energy-intensive, may make it increasingly expensive.
- It is prone to leakage of carbon where companies migrate to other countries with fewer regulations. Choosing an experienced attorney for payroll issues will be the perfect choice.
- Financial uncertainty may arise due to fluctuations in the price of permits and regulatory complexity, and administrative costs may be incurred due to compliance obligations by a firm that attempts to operate within emission limits.
Cap and trade can be a flexible and market-based approach to reducing emissions and stimulating innovation, and investing in new sustainability initiatives. Some of the industries might find it hard, but careful policy formulation and the readiness of businesses will help bring to parity environmental advances and economic growth.